Ali žica zvočnika vpliva na kakovost zvoka? Brez mitov, samo dejstva
Avdio dodatki, kot so kabli in žice za zvočnike, so nekaj najbolj predragih in razvpitih stvari, ki jih lahko kupite.
Bi morali porabiti veliko denarja za "čarobno" žico za zvočnike ali avdio kabel? Ali to vpliva na kakovost zvoka vašega domačega ali avtomobilskega avdio sistema?
To in še več vam bom povedal jasno in preprosto. Berite naprej!
Hitri odgovori:Ali žica zvočnika vpliva na kakovost zvoka?
Hitra dejstva o žici zvočnikov in kakovosti zvoka- V normalnih okoliščinah je odgovor NE:žica zvočnika ne vpliva na kakovost zvoka. Vendar pa lahko v nekaterih primerih (razloženo v nadaljevanju) kakovost zvoka ali glasnost nekoliko vplivata.
- Ni podatkov iz znanstvenih testov, ki bi podprli (zavajajočo) idejo, da "posebne" ali "avdiofilske" žice za zvočnike ali dragi kabli naredijo opazno razliko v primerjavi s cenovno dostopno, kakovostno žico za zvočnike pravilnega premera. 99,9 % časa gre za neutemeljene trditve in razlika res ni pomembna!
- Uporaba nestandardne žice ali kablov namesto žice za zvočnike lahko povzroči spremembe zvoka, čeprav zelo majhne. Predolga ali druga žica z visokim uporom lahko vpliva na zvok, tako da povzroči padec glasnosti zvočnika in nekatere druge podrobnosti.
- Za najboljše rezultate ne navijajte dolgih žic zvočnikov, saj lahko to ustvari induktivnost, ki zmanjša nekatere zvočne frekvence, kot to počne kretnica.
- Žica med kretnicami zvočnikov in zvočniki naj bo dokaj kratka. Predolga žica do kretnice in na zvočnikih lahko povzroči spremembo obnašanja kretnice in spremeni zvočni odziv zvočnika.
Avdiofilske in opevane žice in kabli
Eden največjih problemov, ki sem jih videl v preteklih letih, je količina navdušenja in pretiravanja, ki se uporablja za prodajo predragih kablov vseh vrst:žice za zvočnike, avdio kabli (kot so kabli RCA), video kabli in celo računalniški in podatkovni kabli.
Tudi ni omejeno na uporabo domačega zvočnika ali videa – veliko jih je bilo tudi v svetu avtomobilskih stereo naprav.
Fantastični zvočni kabli in žice temeljijo na neumnosti
Podjetja in avdiofili pogosto trdijo, da njihovi dragi kabli ponujajo boljši zvok zaradi neke vrste ezoterične, modne tehnične prednosti. Težava je v tem, da ni znanstvenih testnih podatkov, ki bi to podprli. Večino časa gre le za trženje za večji dobiček.
Ko gre za elektroniko, so avdio dodatki, kot so priključni kabli RCA, kabli za slušalke in kabli za zvočnike, ena najbolj donosnih kategorij za trgovce!
Znanost o zvočniških žicah in kakovosti zvoka
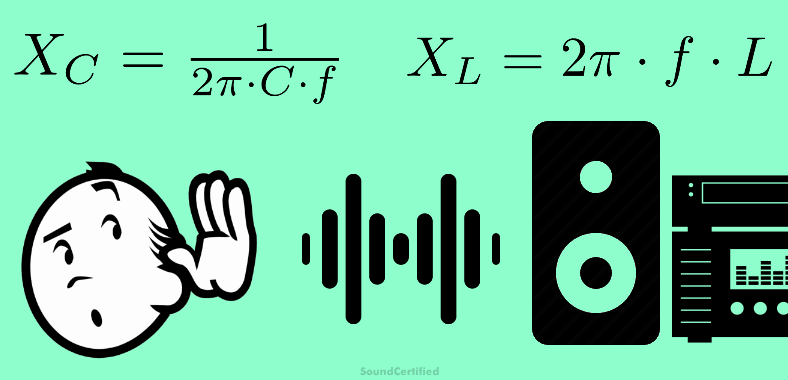
Tukaj je seznam razlogov, zakaj ne boste opazili nobene razlike v kakovosti zvoka zaradi žice zvočnika. Obstaja nekaj izjem, ki niso tipične in jih bom razložil pozneje.
Dejstva o kakovosti zvoka žice zvočnikov:
- Čeprav je res, da ima veliko električnih komponent in prevodnikov kapacitivnost in induktivnost, ki lahko vplivata na zvok, ima žica zvočnika zelo malo. Veliko manj, kot je potrebno za dejanski vpliv na kakovost zvoka in frekvenčni odziv sistema zvočnikov.
- Stvari, kot so zmogljivost zvočnikov, induktivnost zvočne tuljave, kretnice zvočnikov in drugo, imajo veliko večji vpliv na kakovost zvoka – pravzaprav več stokrat večji.
- Žice zvočnikov so sestavljene iz snopa tankih vodnikov, ki se med seboj dotikajo, kar ohranja kapacitivnost in induktivnost na tako majhni ravni, da je za zvok zanemarljiva. Druge vrste kablov (kot so individualno izolirani vodniki) lahko vplivajo na zvok – vendar niso žice za zvočnike.
- Pojav električnega prevodnika, znan kot učinek kože, ne velja za zvočno frekvenčno območje. To ni zaskrbljujoče, dokler se ne ukvarjate z veliko višjimi frekvencami (megaherci in višji razponi). Zvočne frekvence segajo od približno 20Hz do 20kHz.
- Čeprav je res, da so bili opravljeni testi slepega poslušanja, da bi poskušali "dokazati", da posebne zvočne žice ali kabli ljudem zvenijo bolje, tega nikoli ne morejo dokazati. Pravzaprav so testi skoraj vedno zelo pomanjkljivi in nimajo trdnih znanstvenih podatkov o zvočnih testih, ki bi jih lahko podprli. Še huje, učinek placeba vpliva na test, poleg tega pa imajo ljudje različne ravni sluha.
- Mernik, ki ga potrebujete, je odvisen od moči, ki jo dovaja vaš ojačevalnik ali stereo, in dolžine.
- Debelejša žica zvočnikov ima manjši upor, kapacitivnost in induktivnost v primerjavi s tanko žico, saj imajo večjo površino preseka (večja prevodnost/manjši upor).
Razložen električni upor, kapacitivnost in induktivnost žice zvočnika
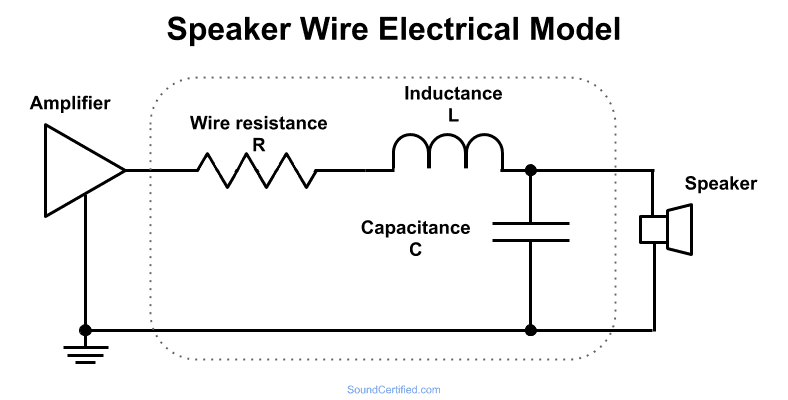
Diagram, ki prikazuje model, kako si lahko zamislite žico za zvočnik ali druge prevodnike. Žica ima v sebi zelo majhno količino upora, induktivnosti in kapacitivnosti.
Žico za zvočnike si lahko predstavljate, tako kot druge električne žice, kot sestavljeno iz upora, induktorja in kondenzatorja, saj imajo skoraj vsi prevodniki vsaj majhen košček vsakega. Upori nasprotujejo toku električnega toka in povzročijo izgubo nekaj napetosti.
Kondenzatorji in induktorji so kot upori, vendar se njihov "upor" (v tem primeru imenuje impedanca) spreminja s frekvenco. Because of it, they’re bad to have in wires that carry an alternating current (AC) electrical signal like music, but extremely useful in things like speaker crossovers.
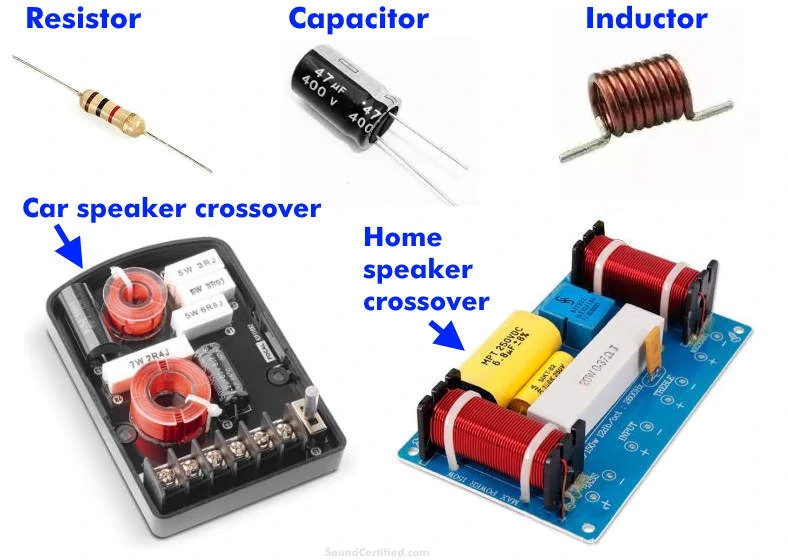
You might be thinking, “If speaker wire has some inductance and capacitance, wouldn’t that hurt the sound? ”
The answer, in this case, is no.
That’s because unlike speaker crossovers where we use large values of capacitors and inductors to filter out or block certain sound ranges to speakers, speaker wire has an incredibly tiny amount. Certainly not enough to have any real effect in most cases.
For example, we could use a capacitor in line with a tweeter to block distorting &damaging bass from reaching it. That’s possible because the impedance (or resistance to current flow) decreases with the frequency, meaning that lower frequencies get reduced a lot and effectively filtered out.
Even basic speaker wire is good!
In the case of speaker wire, if the capacitance were a high value it would be possible for higher frequencies that reach the speaker to be greatly reduced &cause a poor sound quality.
Likewise, if the inductance were high enough to matter it could affect sound quality too. As I mentioned before, however, speaker wire has very low values of each. Ordinary lamp power wire (extremely similar to 18AWG or 16AWG wire) has only about 10-20pFarad capacitance per foot, give less than 1% loss in the audible range for a 50 foot length.
(For comparison, a picoFarad is .000 000 000 001, or a billionth of a Farad unit of capacitance. Capacitors used in audio speaker systems are around a few hundredths of a Farad.)
What is in speaker wire?
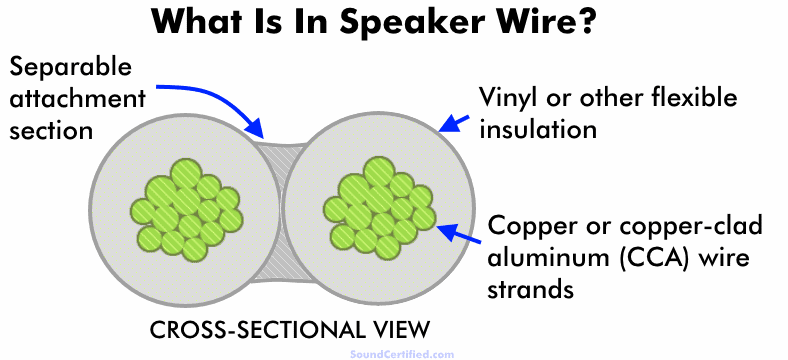
Speaker wire is made up of fine strands of wire, usually copper or copper-clad aluminum (CCA), that are bundled together and electrically separated from each other inside flexible insulation. Other kinds exist too, like those that are also bundled with a thin shield or other special features.
The insulation usually has a thin section in the middle which can be torn easily for separating the wires when stripping it, connecting it, and so on. Most of the time one wire is marked with a positive indicator of some kind.
Speaker wire vs electrical wire
Both electrical hookup wiring (similar to lamp cord) and those sold for speakers often use small strands of conductors and flexible insulation. In fact, in many cases, you can use either. However, you can find audio wire that’s even more flexible and has its polarity marked with red or black as well as printing. Some also have even finer copper conductors to make installation easier around tight spaces or curved areas such as cars and trucks.
Does splicing affect sound quality?
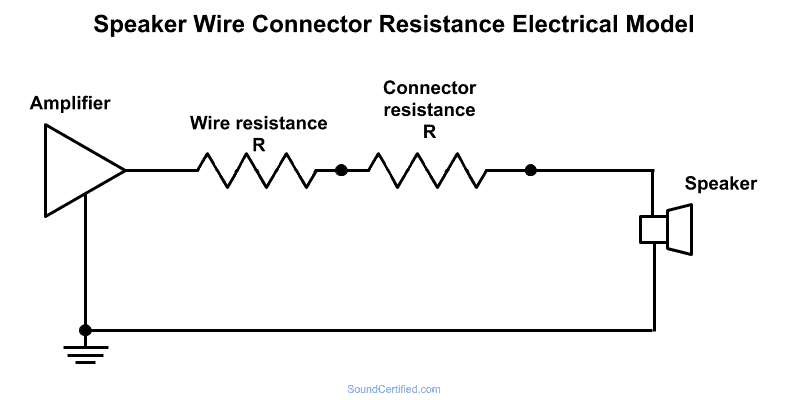
This diagram, like the speaker wire electrical model, shows how you can think of a speaker wire connector. Both wire conductors and connections do have some resistance, although a tiny amount that’s negligible when used correctly. Sound quality isn’t a problem unless there’s an unusually bad connection.
Adding a connector to speaker wiring by splicing, either by soldering, crimp connectors, or other ways doesn’t normally affect sound quality . It can’t – it’s just another path for the flow of power &and the audio signal to flow through.
However, it is possible for an unusually poor connection to have a bad enough resistance that the speaker could have noticeably less volume &power loss. That’s because when a very bad connection causes a high amount of resistance to the flow of current, it also causes a large voltage drop across it, too.
That means less power is available to the speaker than normally would be at the same volume setting. It’s a waste of power.
To avoid this:
- Always use a high-quality connection for speaker wire splices like when extending existing wire. Soldering is the best of all, but good quality crimp connectors are excellent too.
- Wire connection strips (wire terminal barrier strips) with clean nickel or other plated metal contacts are suitable as well for speaker systems.
- Gold plating is not important and you won’t hear the difference.
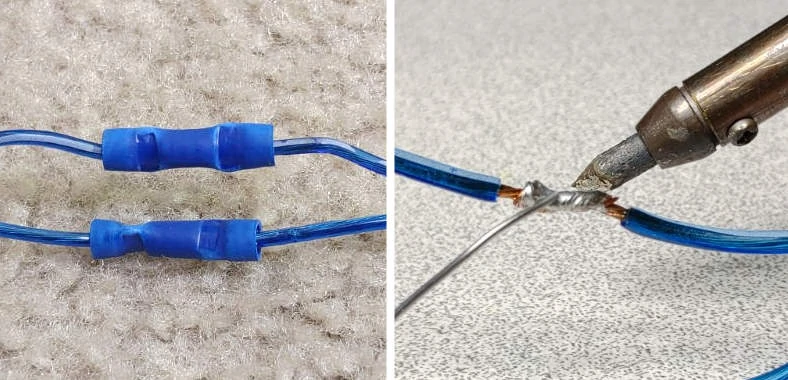
Good quality crimp connectors (left) and soldering (right) are great choices for speaker wire.
The most important thing is to make a tight &clean connection with great wire-to-wire contact.
In some cases like marine &boat use, connectors can corrode &galvanize, causing other issues that do limit sound quality. That’s much less common, however. (In that case, using an anti-corrosion liquid or spray can keep the wire from getting to that point)
TIP: When stripping insulation to expose bare wire you can prevent oxidation over time by “tinning” it (tinning speaker wire means using a soldering iron to flow solder through the exposed conductors and coat them.)

A good option that’s both affordable, simple to use, and makes a great connection is a banana plug pair if your stereo system can use them.
Does the length of speaker wire affect the sound?
It’s definitely possible to lose sound quality a little bit by using a wire or cable length that’s excessively long or not large enough.
To je zato, ker:
- A much greater speaker wire length (say 50+ feet [15.2m], especially 100ft [30m] or more) has more resistance and can cause a small volume &power drop, especially at maximum amplifier power levels. It can also affect a parameter called the damping factor, although it’s not normally an issue.
- Very long lengths of wire will have more capacitance that can slightly affect the frequency response at the speaker. It depends on the particular wire.
- It depends on the power because more power means higher amps pass through the conductors. A lower speaker impedance like 4 ohms or 2 ohms will draw more current than a higher impedance like 8 ohms for the same power.
Unfortunately, even if you’re technically inclined, almost no speaker wire makers offer any technical specs to help you figure out what you can expect for very long lengths. We can, however, use the American Wire Gauge (AWG) standard to know the resistance per foot for most stranded wire.
How long can you run speaker wire without impacting quality?
The length depends on a few things &the AWG size (wire gauge) you’re using. There are a few things that make a big difference:
- The speaker’s impedance. This is usually 6-8 Ohms for home stereo speakers and 4 or sometimes 2 for car audio.
- Amplifier power level you’ll use.
Here’s a basic wire size &length chart to help.
Simplified speaker wire size &length table
| Velikost žice | Priporočeno za |
|---|---|
| 18 Ga. | Car and home speakers up to 25 ft with average power levels (50W RMS and below) |
| 16 Ga. | Longer speaker runs for car &home stereo speakers; Moderate power subwoofers (under 225W) |
| 14 Ga. | Long (100ft+) speaker runs or higher power applications such as high-power 2 or 4 ohm subwoofers. |
This does make a few assumptions, though:most people almost never use their amplifier &speakers at maximum power &volume, so you’re generally fine with the recommendations listed here.
Also, most people do not run extra pairs of speakers in parallel on the same wire which would require wire 2 gauges bigger due to twice the power (and electrical current) being supplied on the same wire.
To keep the sound quality good &power loss to a minimum, for longer lengths go up at least two gauges in wire size for 50 feet or above. Example:when using 18AWG wire normally, go up to a thicker wire (Ex.:18AWG->16AWG->14AWG) for less resistance and to avoid wasted power.When running it a relatively short distance with low to average power (for example to a rear speaker pair in your home or car) don’t stress out over it.
Does using small speaker wire affect sound quality?
Using a thin wire won’t exactly affect sound quality – meaning you won’t hear a noticeable difference – but it can cause you to waste power and lose speaker volume. Typically, most people need about 18AWG wire for speaker systems up to 50W for 4 ohm speakers &about 100W for 8 ohm speakers in relatively short distances (25ft or less).
One thing to bear in mind is that you can’t use copper clad aluminum (CCA) wire for the same power levels as you can copper wire as you’ll see below.
Copper-clad aluminum vs copper speaker wire quality differences
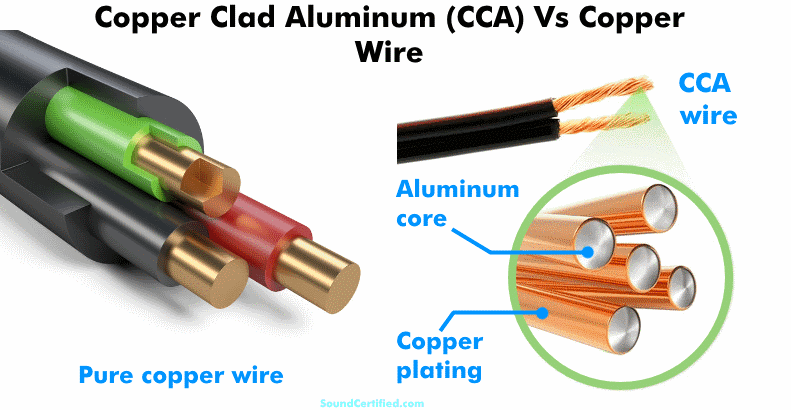
Copper clad aluminum (CCA) wire has, in the last few years, become more and more common as the price of copper wiring has gone up. To je ena tistih "malenkosti", ki jih pri nakupu morda ne poznate in vam jih podjetja ne povedo.
Unlike pure copper wire, copper-clad aluminum uses an aluminum wire core with a thin copper plating . Od zunaj je zavajajoče videti enako zaradi prevleke.
Aluminum offers a lighter weight and lower cost than copper, so it’s at first glance it may seem like a great way to replace more expensive copper wiring. However, there’s an important difference that wire makers often won’t tell you!
How good is copper-covered aluminum speaker wire?
The good news is that CCA wire has the same sound quality as copper wire, meaning it’s fine for great sound. The problem is that aluminum isn’t as good of an electrical conductor as copper.
Aluminum has only 61% of the conductivity of copper (in other words, it has 39% more resistance) meaning it will take larger aluminum wires to get the same wire quality.
What to know before buying CCA speaker wire
V večini primerov, na primer pri povprečnem poslušanju in tipičnih ravneh moči, to v resnici ni problem pri vsakodnevni uporabi. However, if you’re going to drive speakers at higher power levels or want the absolute best for your money, you’ll need to be sure to look for packaging that clearly states 100% pure copper.
Otherwise, copper-clad aluminum will work just as well if you follow this rule:when buying CCA speaker wire, to get the same quality as true copper cable go up one gauge in size.
For example, to replace 18 gauge copper speaker wire use a 16 gauge CCA wire.
Cases where speaker sound response, volume, or quality can be affected
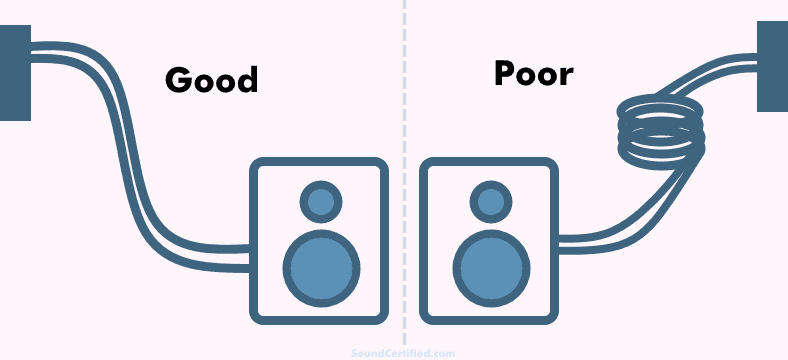
For best results, do not coil up excess lengths of speaker wire. Keep the free wire straight &curved instead. Coiled wire can act as an inductor and potentially affect the sound in some cases. (An inductor is a coil of wire that builds magnetic fields)
There are some cases where using wire the wrong way (or using the wrong kind type) leads to bad performance:
- Using non-standard wire or cable as speaker wire
- Winding long lengths of wire into a loop, creating a coil (creating an inductor basically)
- Breaks or cuts in speaker wire that cause problems with power flow
- Poor connections like twisting wire together instead of using a proper connection
- Heavily oxidized wire
- Loosely connected speaker box posts or terminals
To avoid nicking the wire inside, avoid using a razor or utility knife to strip wires. Use a stripper or other tool instead.
Exposed copper wire can oxidize badly over time and cause a very poor connection, especially after being exposed to moisture and especially other air outdoors. Be sure to check and cut &re-strip if necessary or use a nice clean connection or solder to eliminate this. Note that covering it with electrical tape isn’t enough.
Speaker wire terminals in speaker boxes can become loose and get hot once the connection is bad enough, causing a lot of power to be lost and give poor sound. It’s a great idea to check and tighten or replace terminals if you’re having sound quality issues.

Even though you may be tempted to save money by reusing some extra wire or that instrument cable you’ve got lying around, cables are often bad choices for speaker wire. Coaxial cable, for example, can have higher capacitance and cause sound quality problems.
Microphone and network cables usually have much smaller conductors that can’t carry the power you need for speakers, as well as being more susceptible to break if they’re solid conductors.
More great speaker wire articles
I’ve got more helpful articles related to speaker wire, too:
- Learn how to fix speaker wire in your car!
- What size speaker wire you need including a speaker wire power chart
- Ran out of enough wire? Here’s how to extend &lengthen speaker wire the right way.
- Learn the basics of how to connect speaker wire.
- Here’s a helpful speaker wiring diagram guide for everyone.
